Primarily this type of bond occurs between elements that fall close to each other on the periodic table of elements yet it is observed between some metals and nonmetals. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.

Chemical Bonding Lesson Plan A Complete Science Lesson Using The 5e Method Of Instruction Kesler Science Science Lessons Chemical Bond Covalent Bonding
Valence Electrons.

. The enthalpy of a given molecular interaction between two non-bonded atoms is 1 - 10 kcalmole 4 - 42 kjoulemole which in the lower limit is on the order of RT and in the upper limit is significantly less than a covalent bond. Thus to increase positive charge electrons must be removed. The Be-H bond is a polar covalent bond still the BeH2 molecule is nonpolar due to its linear shape and zero net dipole moment.
Non-polar covalent bond Formed by identical atoms. This is due to the mechanism of this type of bond. Thus s-orbitals have a spherical symmetry surrounding a single nucleus whereas σ-orbitals have a cylindrical symmetry and encompass two or more nuclei.
EgCl 2 O 2 N 2 etc. Thus an oxidizing agent must oxidize. Octet Rule Atoms of different elements take part in chemical combination in order to complete their octet or to attain the noble gas configuration.
A an ionic bond c a covalent bond b a hydrogen bond d a coordinate. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons and positively charged metal ionsIt may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties. The shape of BeH2 is linear with the sp hybridization of the beryllium atom.
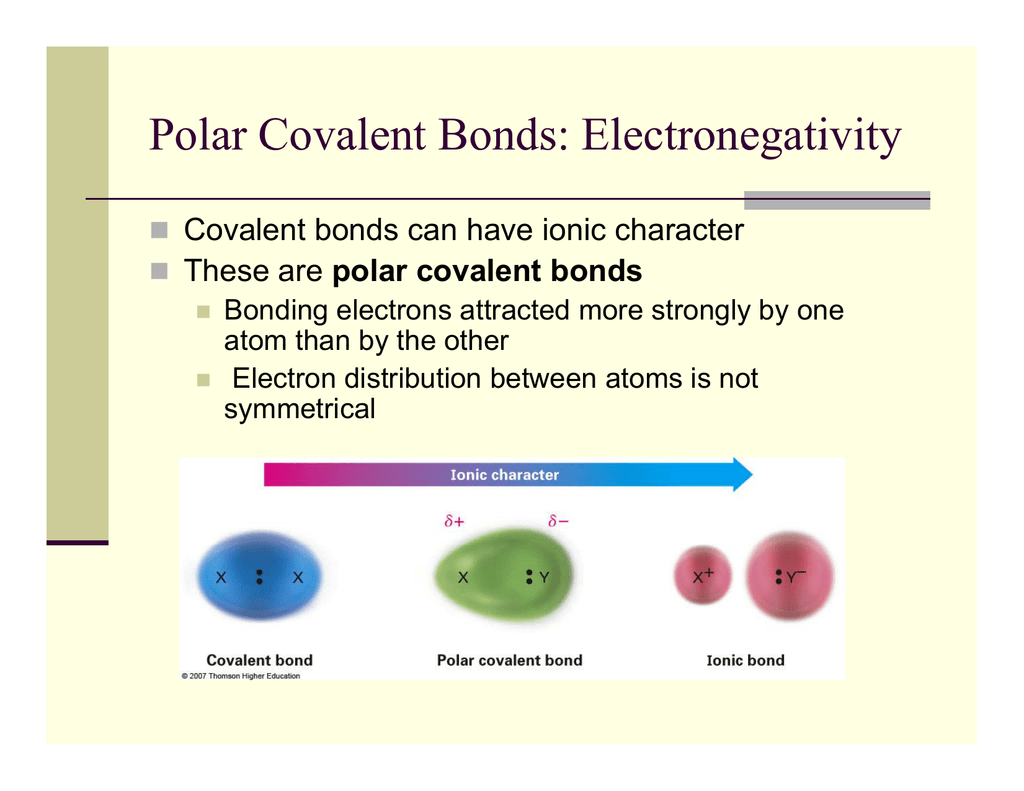
The difference in electronegativity. The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity. The tendency of an atom or molecule to draw electrons towards itself form dipoles and thus form bonds.
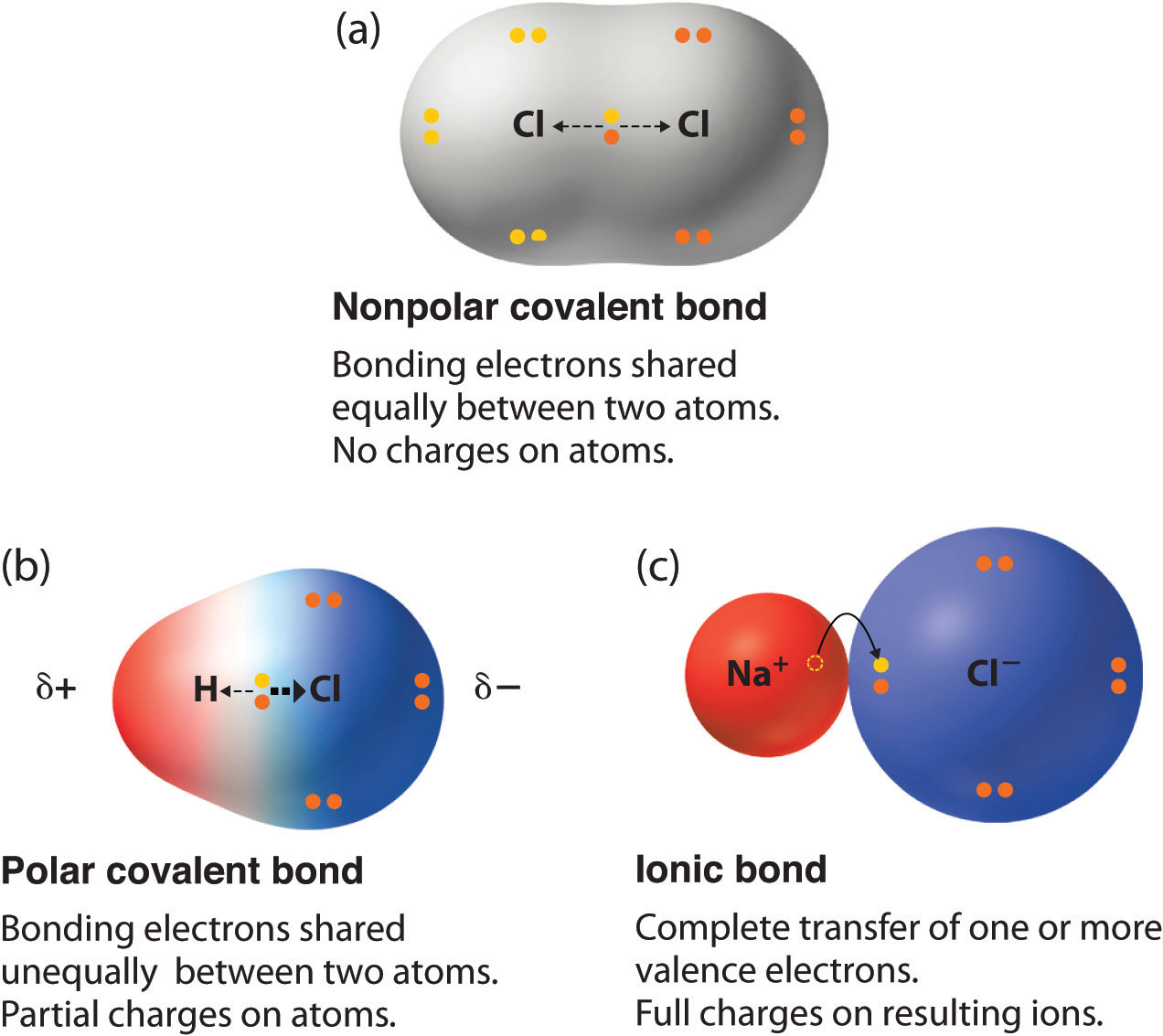
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The hydrogen bond is one of the strongest intermolecular attractions but weaker than a covalent or an ionic bond. If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical as in H 2 Cl 2 and other diatomic molecules then the electrons in the bond must be shared equallyWe refer to this as a pure covalent bondElectrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus.
Access the answers to hundreds of Chemical bond questions that are. Chemical Bond Questions and Answers. D covalent because electrons are transferred 9 Which type of bonds are formed when calcium atoms react with oxygen atoms.
A hydrogen b coordinate covalent c polar covalent d ionic 10 Which type of bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. There are different ways to represent a compounds structural. Covalent bonds formed between atoms of the same kind are usually non-polar and the shared electrons are equidistant from both atomic nuclei.
The bonding MO is occupied by two electrons of opposite spin the result being a covalent bond. Start studying Chem 5. In order for it to oxidize something else it must itself be reduced.
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for holding together DNA proteins and other macromolecules. In brief the BeH2 molecule is a Lewis acid owing to the incomplete octet of the beryllium atom which can be observed from its Lewis structure. A covalent bond also known as a molecular bond involves the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
The ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity. Now we discuss the movement of electrons. In pure covalent bonds the electrons are shared equally.
In polar covalent bonds the electrons are shared unequally as one atom exerts a stronger force of attraction on the electrons than the other. Defining oxidation as the increase in oxidation state eg from 1 to 2 we see that charge is becoming more positive. Start studying BIO CH3.
It is always good to have choices and the same goes with how we draw structural formulas. If the difference in electronegativity is between 04 and 17 the character of the bond is polar covalent. The notation used for molecular orbitals parallels that used for atomic orbitals.
If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 17 the character of the bond will be ionic. Polar covalent bonds are charged positive as well as negative poles whereas non-polar covalent bonds are not charged. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bond The force that holds different atoms in a molecule is called chemical bond.
Get help with your Chemical bond homework.
0 Comments